| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | In the CAST burner, soot particles are formed within a co-flow diffusion flame due to the hydrocarbon pyrolyse that takes place as a consequence of the heat provided by the oxydation at the flame front. The CAST burner enables the soot particles to escape from the flame without contact with oxygen. Subsequently the particle stream is mixed with a quenching gas in order to prevent further combustion processes in the particle stream and to stabilize the soot particles. The quenching inhibits condensation in the particle stream at ambient air condition. To dilute the particle stream, compressed air is supplied to the quenched particle stream. | | | | | | 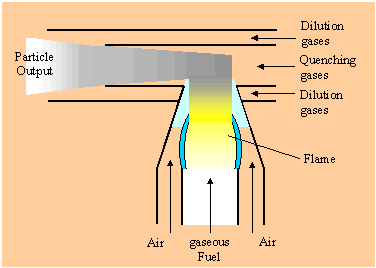
| | | | | | | | Principle of CAST | | | | |
| | |

